Gastroparesis, a condition where your stomach can’t empty itself of food in a normal fashion, can be more than just uncomfortable—it can disrupt your life. When diet changes and medications fail to provide relief, surgery might be the next step. It’s a big decision, but understanding your options can help.
Penn Medicine stands out as one of the few centers in the US offering gastric electrical stimulation, also known as a gastric pacemaker. This innovative surgery has transformed the lives of many patients by addressing the root cause of gastroparesis. Let’s dive into the surgical options available for managing this challenging condition, including the pros and cons, to help you make an informed decision.
Key Takeaways
- Gastroparesis is a condition where the stomach empties too slowly, leading to symptoms like nausea and abdominal pain; when diet and medication fail, surgery may be considered.
- Several surgical options are available for gastroparesis, including gastric electrical stimulation (GES) for severe chronic symptoms, and procedures like gastrostomy venting and pyloroplasty for improving gastric emptying.
- Gastric electrical stimulation (GES), offered at specialized centers like Penn Medicine, involves implanting a device that sends electrical pulses to the stomach, showing promise in managing nausea and vomiting for those unresponsive to other treatments.
- Alternative surgical procedures such as gastrojejunostomy and gastrectomy are aimed at bypassing or removing parts of the stomach to facilitate digestion and relieve symptoms in severe cases.
- Each surgical option has its pros, such as improved symptom management and nutrition absorption, and cons, including potential risks of complications and the need for adjustments in lifestyle.
- Decision-making regarding surgical intervention for gastroparesis should involve a thorough discussion with healthcare providers, considering the severity of symptoms and overall health.
Overview of Gastroparesis
Gastroparesis, often referred to as delayed gastric emptying or stomach paralysis, is a condition where your stomach takes longer than normal to empty its contents into the small intestine. It results from damage to the vagus nerve, which regulates the digestive system. This condition can lead to a variety of symptoms, including nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, and a feeling of fullness soon after starting to eat. When the standard interventions like diet modifications and medications don’t alleviate your symptoms, surgery may become a consideration.
How to Treat Gastroparesis
First, you need to get an accurate diagnosis. The diagnosis of gastroparesis involves several tests. One critical test measures the electrical pulses in your stomach that cause contractions. Placing electrodes on the skin can accurately detect these pulses and, alongside a gastric emptying test, determine the cause of gastroparesis in some cases.
Unfortunately, there’s no cure for gastroparesis, but multiple treatment options can control symptoms such as chronic vomiting and nausea. The key to managing gastroparesis lies in symptom control and enhancing the quality of your life.
Treatment approaches for gastroparesis include:
- Diet Modification: Altering your diet to include foods that are easier to digest can significantly reduce symptoms.
- Prokinetic Drugs: These medications help speed up stomach emptying.
- Antiemetic Drugs: These drugs reduce nausea and vomiting.
- Enterra Therapy (Gastric Electrical Stimulation): A gastric pacemaker sends mild electrical pulses to help control nausea and vomiting.
- Enteral Nutrition: When oral eating doesn’t supply adequate nutrition, liquid food is delivered into the digestive tract through a feeding tube.
- Gastrectomy: In severe cases, part or all of the stomach might be surgically removed or bypassed.
For severe cases where conventional treatments fail, surgical interventions like the insertion of a Gastrostomy-Jejunostomy (GJ) tube might be necessary. This feeding tube enables nutrition to bypass the stomach and enter the small intestine directly, providing an alternative way to manage the condition when gastroparesis severely impacts your life.
Surgical Options for Gastroparesis
When you’re facing gastroparesis, understanding your surgical options is crucial. As this condition often proves chronic, finding effective management strategies is vital for maintaining quality of life. Surgical interventions may become necessary when other treatments fail to provide relief. It’s essential to know the available surgical procedures, tailored to address the severity and specific symptoms of gastroparesis.
One of the initial surgical options includes gastrostomy venting. This procedure is designed to prevent the buildup of excess air and fluids in the stomach, providing immediate relief from discomfort.
Another common surgery is pyloroplasty, which widens the lower part of the stomach, facilitating easier passage of food.
For more complex cases, a gastrojejunostomy may be recommended. This connects the stomach to the jejunum, part of the small intestine, helping bypass areas of obstruction or delay.
In situations where large portions of the stomach are affected, a gastrectomy might be necessary, either removing part or the whole stomach. Additionally, a jejunostomy can be crucial for patients needing direct nutritional support. This involves the insertion of a feeding tube directly into the jejunum.
Patients with severe symptoms and those who have not responded to medical therapy often require these surgical interventions. The choice between a gastric electric stimulator (GES) placement and pyloric intervention depends on specific symptoms like nausea and vomiting, and the extent of gastric emptying delay.
| Patient Symptoms | Recommended Procedure |
|---|---|
| Predominant nausea and vomiting | Gastric Electric Stimulator (GES) |
| Severely delayed gastric emptying | Pyloric Intervention/Combined Proc |
Understanding the nuances of each surgical option allows for a more informed decision when working with healthcare providers to manage gastroparesis effectively.
Gastric Electrical Stimulation (Gastric Pacemaker)
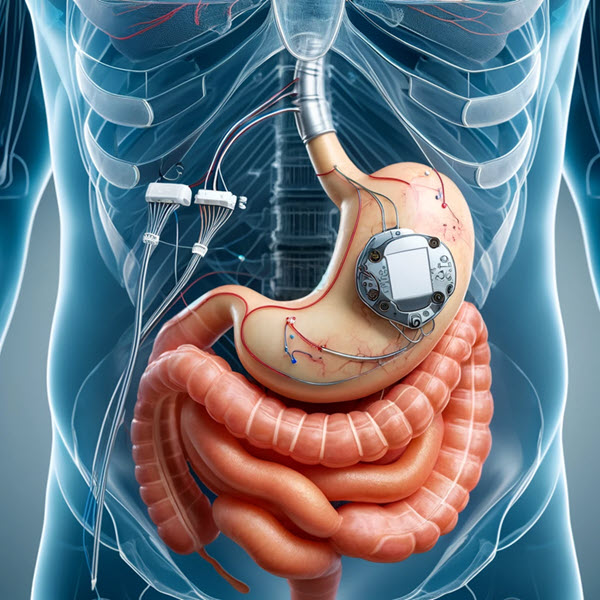
Gastric electrical stimulation works by sending high-frequency electrical pulses to the stomach at 12 cycles per minute, targeting the muscles involved in gastric emptying. The device, akin to a heart pacemaker, is implanted during a surgical procedure either through laparoscopy or laparotomy. Wires are carefully placed in the stomach’s muscle layer, specifically at the greater curvature, and connected to a stimulator tucked away in a subcutaneous pocket in the abdomen. This approach has gained FDA humanitarian approval for its role in managing chronic refractory nausea and vomiting associated with diabetic or idiopathic gastroparesis.
| Initial Study | Result |
|---|---|
| Number of Patients | 26 |
| Reported Improvement | 20 |
| Decrease in Symptoms | Nausea and vomiting improved |
During a subsequent double-blind crossover design study involving 33 patients, the stimulator was alternately turned on and off, highlighting its influence on symptoms management. While it shows promise in alleviating nausea and vomiting, it’s important to note that not all patients might find the relief they seek. A small subset, as observed in the initial studies, may still require further interventions, such as total gastrectomy, due to unsatisfactory outcomes or complications like erosion or infection related to the device.
Gastric electrical stimulation represents a significant step forward in gastroparesis treatment for those who have not found success with other modalities. With advancements continuing to unfold, it’s a topic worth discussing with your healthcare provider if you’re searching for alternatives to manage severe gastroparesis symptoms.
Each of these procedures comes with its own benefits and risks, and it’s essential to discuss these in depth with your healthcare team. The right approach for you will depend on the severity of your symptoms, your overall health, and how gastroparesis is affecting your quality of life.
Pros and Cons of Surgical Interventions
When considering surgical options for gastroparesis, it’s crucial to weigh the benefits and risks associated with different procedures. Each intervention comes with its unique set of pros and cons, directly impacting your decision-making process and overall health outcome.
Pros
Surgical interventions for gastroparesis, such as gastrostomy or pyloroplasty, offer relief from severe symptoms that don’t respond to medication or dietary changes. These procedures can significantly improve quality of life, allowing for better nutrition absorption and reducing hospital visits due to complications. For instance, gastrojejunostomy facilitates direct feeding into the small intestine, bypassing the sluggish stomach. Similarly, gastrectomy, although a last resort, might be necessary to remove parts of the stomach that are irreversibly damaged, offering a potential solution for severe cases.
- Better symptom management
- Improved nutrition absorption
- Reduced hospital visits
Cons
However, these surgeries aren’t without their downsides. Complications can arise, such as postoperative infections, the need for additional surgeries, or, in rare cases, erosion of device components through the skin when using gastric electrical stimulators. Each surgical option requires careful consideration of these risks. For example, the gastric electric stimulator, while beneficial for some, may lead to complications like skin erosion or hematoma. It’s also worth noting that surgeries like pyloroplasty or gastrojejunostomy involve a significant recovery period and adaptation to new dietary habits.
- Risk of complications
- Potential need for further surgeries
- Recovery and adaptation period
Understanding these aspects is vital for making an informed decision about pursuing surgical treatment for gastroparesis. It’s important to engage in thorough discussions with your healthcare provider, assessing the severity of your symptoms, and considering your overall health to determine the most suitable option.
Conclusion
Choosing the right surgical intervention for gastroparesis is a crucial step towards better health and improved quality of life. It’s essential you weigh the benefits against the potential risks and consider how each option aligns with your specific health needs. Remember, the goal is to enhance your symptom management and overall well-being. Engaging in open, detailed conversations with your healthcare team will guide you to the most appropriate decision for your situation. With the right approach, you can navigate the complexities of gastroparesis surgeries and move closer to finding relief and regaining control of your health.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the surgical options for managing severe gastroparesis symptoms?
Surgical interventions like gastrostomy (stomach tube placement), pyloroplasty (opening the pylorus which connects the stomach to the small intestine), gastrojejunostomy (connecting the stomach directly to the jejunum, part of the small intestine), and gastrectomy (partial or total removal of the stomach) are options for managing severe gastroparesis symptoms. These procedures aim to improve symptom management, enhance nutrition absorption, and reduce hospital visits.
What are the risks associated with gastroparesis surgery?
The risks of surgery for gastroparesis include postoperative infections, the potential for additional surgeries, and the need for recovery and dietary adjustments. Like all surgical interventions, these procedures carry inherent risks, emphasizing the importance of thorough pre-operative discussions with healthcare providers.
How can surgical options for gastroparesis improve my quality of life?
Surgical interventions for gastroparesis, such as gastrostomy, pyloroplasty, gastrojejunostomy, and gastrectomy, can significantly improve symptoms, enhance the ability to absorb nutrients, and decrease the frequency of hospital visits. These potential benefits aim to improve overall quality of life by offering better symptom control and nutritional support for individuals struggling with severe cases of gastroparesis.
What should I consider before opting for surgery to manage gastroparesis?
Before deciding on surgery for gastroparesis, it’s crucial to discuss with healthcare providers to understand the potential benefits, risks, and the necessity for postoperative adjustments. Consideration of the severity of symptoms, overall health, and the impact on quality of life is essential. A thorough evaluation will help determine the most suitable surgical option for individual cases.